Chinese Researchers Develop Lipid-lowering Small Compound DC371739
Hyperlipidemia, characterized by increased levels of cholesterol and triglycerides (TGs) in circulation, is a major risk factor for atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease. Lipid-lowering drug statins are currently the main clinical treatment for hyperlipidemia, though they are not suitable for patients with statin intolerance. Therefore, developing non-statin-based cholesterol-lowering small compounds is highly desired.
In a study published in Cell Metabolism, LIU Hong and HUANG He from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, identified the novel target of hyperlipidemia, and developed a novel lipid-lowering small compound DC371739, which showed a promising lipid-lowering effect in vitro and in vivo, as well as good safety and tolerability both in healthy subjects and in patients with hyperlipidemia in the phase one trial.
The researchers proved that DC371739, as a lipid-lowering drug candidate, efficiently reduce the total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and TG in the serum of hyperlipidemic hamsters in a dose-dependent manner. In a spontaneous hyperlipidemic rhesus monkey model, DC371739 can reduce the level of TC and LDL-C in a dose-dependent manner, with an effective dose of 3 mg/kg. Given the good pharmacological profiles, satisfactory pharmacokinetic properties, and low toxicity, DC371739 was selected as a drug candidate for the treatment of hypercholesterolemia.
Mechanistically, compared with other known lipid-lowering reagents, DC371739 acts in a distinct manner. Researchers found that it could physically bind HNF-1α, impeding the transcription of both PCSK9 and ANGPTL3, two genes that are known to contribute to hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia. Moreover, the distinct action mechanism of DC371739 allows its combination with atorvastatin treatment to additively improve dyslipidemia, thus providing a potential alternative therapeutic strategy for individuals with statin intolerance.
Through combination with atorvastatin, a statin drug, the new candidate provides a potential therapeutic strategy for patients with statin intolerance due to its action mechanism that is distinct from other known lipid-lowering reagents.
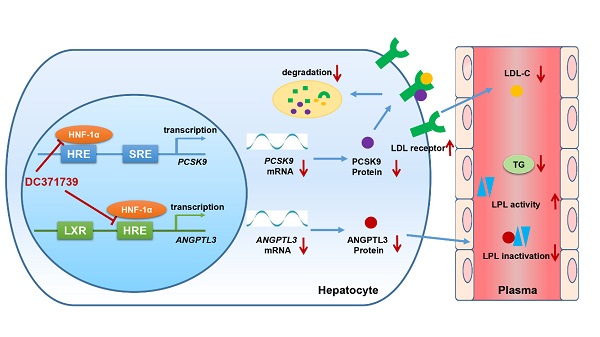
DC371739 regulates PCSK9 and ANGPTL3 transcription by targeting HNF-1α (Image by LIU Hong and HUANG He’s team)
Contact:
DIAO Wentong
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica
E-mail: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn




