Researchers Reconstruct A Whole-Brain Panorama of Multiple Structures in Alzheimer's Disease Mice
To understand the complex pathology of Alzheimer's disease, it is necessary to simultaneously visualize Aβ plaque with its surrounding brain structures at the subcellular level in the intact brain. However, it is rarely achieved owing to technical limitations. Due to spectral overlap of the fluorophore and crossover of fluorescence emission, it is still challenging to detect more than three fluorescent labels using fluorescence imaging techniques.
In a study recently published in Frontiers in Neuroscience, a team of researchers from the Center of Micro-Optical Sectioning Tomography (MOST) and Image Fusion Analysis of the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, visualized the Aβ plaques, nerve tracts and nerve processes, somata, and blood vessels simultaneously in the whole brain of Alzheimer's Disease (AD) mice for the first time, without any specific labelling.
Employing the MOST system, whole-brain Nissl staining, and a customized image processing workflow, the researchers distinguished the characteristic signals of these multiple structures based on the differences in gray values and morphologies. Taking advantage of this workflow, the researchers were able to analyze how the Aβ plaques interact with capillaries, somata, and processes at a submicron resolution of 3D whole-brain scale.
This research provides a novel approach to clearly present various structural information in a whole mouse brain simultaneously, which will facilitate a better understanding of the cerebral anatomical features under the pathological state of AD.
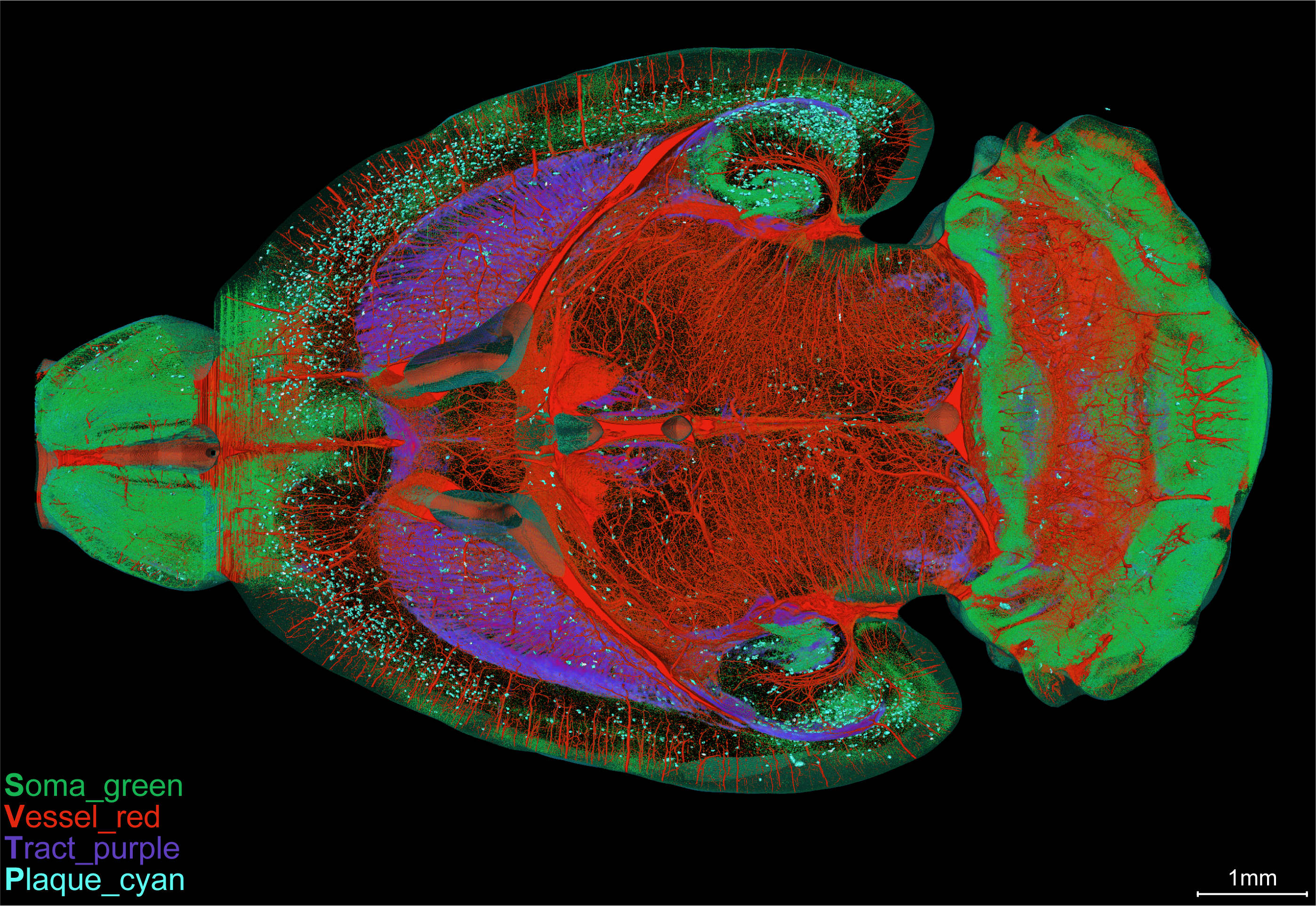
Simultaneous whole-brain visualization of multiple structures in the 5×FAD mice with different structures coded by different pseudo-colors. (Image by MOST_SIMM team)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2022.870520
Link: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnins.2022.870520/full
Contact:
DIAO Wentong
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn




