Researchers Discovered Water-Soluble Zolinium Selectively Modifying Lysine Residues of Peptides and Proteins
Lysine has a high abundance (5.9%) in the human proteome and is involved in important physiological functions. Site-selective modification of lysine residues of target proteins under physiological conditions has broad applications in the field of pharmacy.
The ε-amino group of lysine is easily protonated under physiological conditions, it is very challenging to covalently modify lysine residues of target proteins under physiological conditions. The reported lysine covalent modifiers have poor water solubility and high reactivity, leading to possible problems such as selectivity and toxicity. So far, no rationally designed drug covalently targeting lysine residues has been marketed. There are requirements to develop lysine modifiers with good selectivity, water solubility and low toxicity to meet the needs of various biomedical applications.
In a study published in J. Med. Chem, LI Bo and ZHU Weiliang from the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with Prof. GE Guangbo from Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, designed and developed a new type of lysine modifiers called "Zolinium" based on their 10-year optimization results from the natural product Berberine.
The new water-soluble Zolinium was capable of selectively modifying the lysine residues of the peptidic drugs. At the cellular level, the Zolinium can also be used to map lysine-modified proteins in living cells, and fluorescent molecules with Zolinium warheads can image subcellular organelles such as lysosomes. Protein pooling experiments suggested that site-selective modifications occur primarily in hydrophobic or catalytically active pockets and may be enhanced by the neighboring acidic amino acid residues.
In addition, modification experiments with mixtures of eight different amino acids and different peptides with potentially reactive residues showed that the novel water-soluble Zolinium exhibited good selectivity for the lysine quinolinylation of peptides and proteins, and was highly selective and well tolerated for various functional groups.
Quantum chemistry calculation results showed that compared with that of other reactive groups on various amino acid residues, the reaction of ε-amino group of lysine with Zolinium had the lowest free energy barrier. Since its quinoline ring can be further modified to obtain various derivatives, Zolinium is expected to play an important role in the research of peptides and proteins for specific purposes and protein-lysine modification in living cells.
This new type of water-soluble Zolinium developed in this study can chemically and site-selectively modify lysine in peptides, proteins and living cell proteins, which has potential application in chemical biology and innovative drug research.
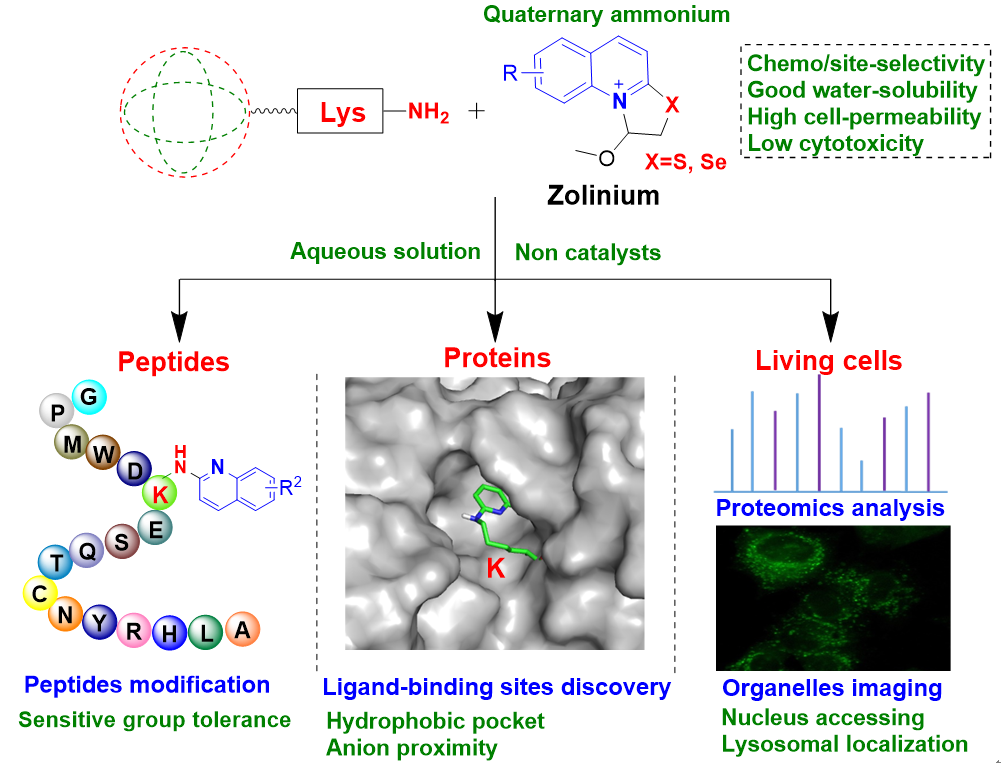
Water-soluble "zolinium" modifies lysine residues of peptides and proteins and its applications at the cellular level (Image by the authors of the JMC paper)
Article: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00937
CONTACT:
DIAO Wentong
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica
E-mail: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn




