Scientists Shed a light on How MiR-629-5p Promoted the Invasion of Lung Adenocarcinoma
A research team from the Center for Drug Safety Evaluation and Research (CDSER) under the Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica has recently published an article titled “MiR-629-5p promotes the invasion of lung adenocarcinoma via increasing both tumor cell invasion and endothelial cell permeability” in Oncogene.
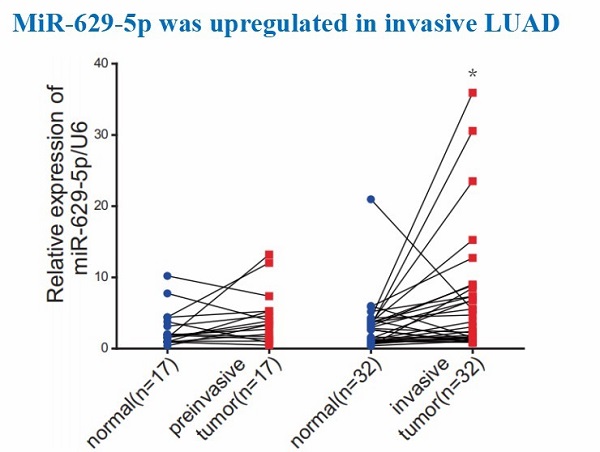
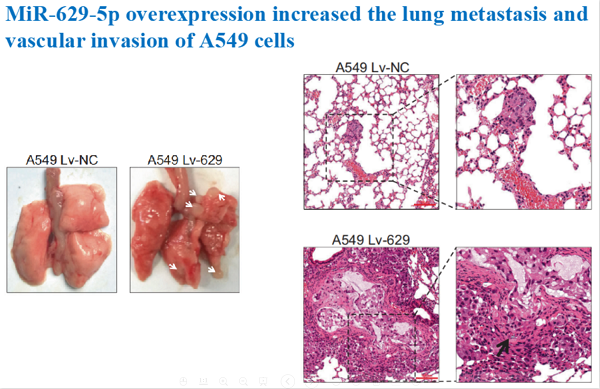
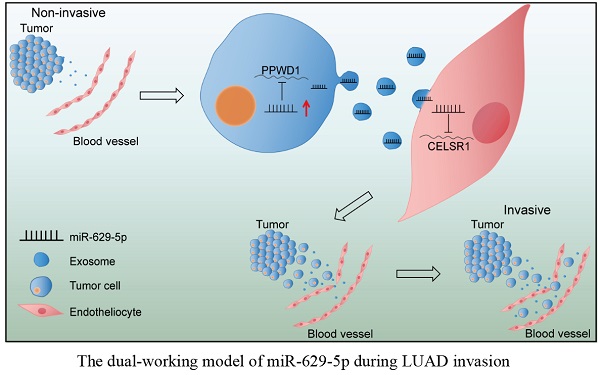
MiR-629-5p belongs to non-coding small RNA,has been identified as a promoter in tumor progression. In this work, scientists revealed that via enhancing the invasiveness of cancer cell itself and exosomally increasing the permeability of endothelial barrier, miR-629-5p promotes the invasion of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD). Further exploration showed that miR-629-5p promotes the cell migration and invasion in LUADs via inhibiting the gene expression level of PPWD1, which has been reported related to tumor metastasis in tumor cells. Besides, miR-629-5p secreted by tumor cells could downregulate CELSR1 in endothelial cells, leading to the increase of endothelial monolayers permeability.
These findings developed a new perspective for understanding the mechanisms of tumor progression, implying a therapeutic option to targeting miR-629-5p using the “one stone, two birds” strategy in LUAD.
This research is a new founding gained on the basis of years of research on non-coding RNA and a fresh achievement yielded from basic research to clinical verification by the CDSER team led by Prof. REN Jin. Prof. HUANG Ruimin also made a great contribution to this work. The first author of this article is Dr. LI Yu, and this work was supported by the National Science & Technology Major Project “Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program” of China.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1228-1
Contact:
Prof. REN Jin
Email: jren@cdser.simm.ac.cn
(Credit: LI Yu)




