Scientists Reveal How Dopamine and Its Activity Regulator Bind to Dopamine Receptor D1
On March 9, 2021, scientists from an international joint team reported the near-atomic structure of dopamine receptor D1 bound with dopamine. In addition, they revealed also the high-resolution structure of D1R with its positive allosteric modulator LY3154207.
The research, published in Cell Research, was accomplished by Prof. XU Huaqiang (H. Eric Xu) from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), together with Prof. Bryan Roth from University of North Carolina Chapel Hill, Prof. ZHANG Yan from Zhejiang University, and their collaborators.
Dopamine (DA) is an important monoamine neurotransmitter involved in the regulation of various physiological functions of the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). DA conducts signal transformation through five dopamine receptors (DRs), namely, D1R, D2R, D3R, D4R and D5R. All the DRs belong to the G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily. Among DRs, D1R is most abundantly expressed in CNS. Dysfunction of D1R is associated with various neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, and drug addiction, making it an important drug target for developing efficient treatments of neuropsychiatric diseases.
For a long time, as the endogenous ligand of D1R, the detail of how DA recognizes and activates D1R was poorly investigated. The cellular activities of D1R agonists, such as DA, can be regulated by D1R positive allosteric modulators (PAMs). However, the mechanisms remain unknown of how PAMs regulate D1R conformation and promote the cellular activity of D1R agonists. To overcome these scientific questions, scientists determined the structures of D1R PAM LY3154207 bound D1R-Gs signaling complexes activated by either DA or a synthetic agonist SKF81297.
In this study, researchers found that the overall interaction patterns of DA and SKF81297 with D1R are similar. The noticeable difference is that DA lacks an extended binding pocket (EBP) that interacts with D1R, which makes its affinity to D1R weaker than SKF81297.
The structures clearly showed the binding pose of PAM LY3154207. LY3154207 molecule lies in the cleft between TM3 and TM4 and right above ICL2 with a boat conformation. Interestingly, researchers found that the binding pose of LY3154207 in this study is different from that obtained by molecular dynamics simulation in previous studies. In addition, the binding mode of LY3154207 in this study is also divergent from the recently reported structure of D1R binding to LY3154207. Through comparing the structures of D1R-SKF81297 in the presence or absence of LY3154207, researchers found that LY3154207 may help keeping D1R in its active state, thereby enhancing the activation efficiency of agonists.
“D1R has long been considered as an efficient drug target for treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. In this study, we present the clear view of human D1R bound to its endogenous agonist dopamine and allosteric modulator LY3154207 compound. Together with the series of D1R structures we published in Cell 1 last month, these structures present a more complete landscape in understanding pharmacology of D1R, and provide multiple templates in designing more efficient and safer drugs treating CNS diseases”, one of the corresponding authors, Prof. H Eric. Xu said.
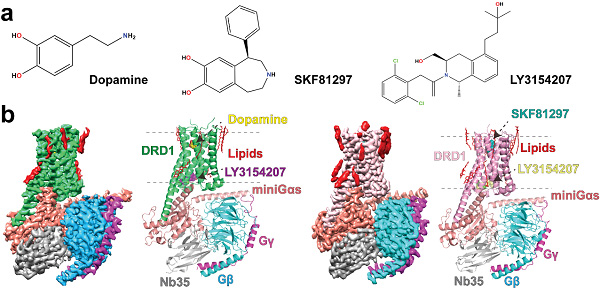
structures of DA or SKF81297 bound D1R-Gs complexes, both in presence of PAM. (Image by H. Eric Xu’s group)
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-021-00482-0
Link to article:https://www.nature.com/articles/s41422-021-00482-0
Contact: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn
References
1. Zhuang, Y. et al. Structural insights into the human D1 and D2 dopamine receptor signaling complexes. Cell 184, 931-942 e918, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.01.027 (2021).




