Researchers Discover Novel Mechanisms of AMPK epigenetically Suppressing Cncer Metastasis
Lung cancer is highly susceptible to metastasis. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) has been implicated as a driver in the dissemination of cancer cells. During EMT, the chromatin landscape is highly changed. Epithelial genes were stably inhibited (marked by H3K27me2/3, H3K9me2/3 and DNA methylation) from an active state, and vice versa to activate mesenchymal genes. Therefore, targeting epigenetic modification is an effective strategy to overcome tumor metastasis.
In a study published in Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (STTT) on March 6, a team of researchers led by LI Jia from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with ZANG Yi from Lingang Laboratory and SHI Hong from Shanghai Pulmonary Hospital, provided mechanistic insights into AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) epigenetically suppressing cancer metastasis via downregulating H3K9me2.
Researchers found that AMPK activation epigenetically could relieve the H3K9me2 mediated silencing of epithelial genes and inhibit lung cancer metastasis. Mechanistically, they identified PHD finger protein 2 (PHF2), a Jumonji C domain-containing histone-lysine demethylase (KDM) that removed H3K9me2, as a direct phosphorylation substrate of AMPK. AMPK phosphorylated PHF2 at S655 to enhance its histone demethylase activity and to trigger epigenetic reprogramming of epithelial genes, thus suppressing lung cancer metastasis. Consistent with these results, the AMPK activator metformin suppressed lung cancer metastasis via the AMPK-PHF2 axis. Importantly, higher PHF2-S655 phosphorylation level correlated with better survival in lung cancer patients.
Together, these findings demonstrates a mechanism of AMPK downregulating H3K9me2 modification and provides new insights of PHF2 as the potential epigenetic target in lung cancer metastasis. Thereby the research promotes the clinical application of metformin to suppressing tumor development.
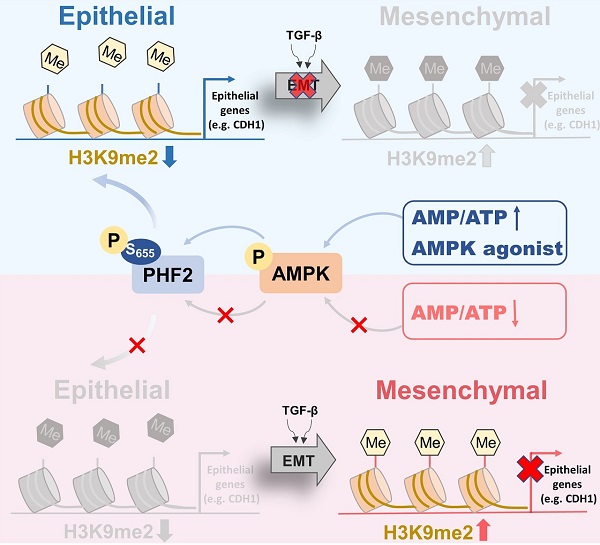
schematic depicting the molecular mechanism through which AMPK epigenetically inhibits lung cancer metastasis (Image by Dr. DONG Ying)
Contact:
DIAO Wentong
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica
Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn




