Researchers Reveal AI Platform KinomeMETA for Kinase Multi-Target Activity Screening
Protein kinases are implicated in a range of serious diseases, prompting the development of targeted therapies. However, due to the high degree of similarity among kinases, it is crucial for researchers to systematically assess the polypharmacology of kinase small molecule inhibitors.
In a study published in Nucleic Acids Research on May 16, a research team led by LI Xutong, ZHENG Mingyue and ZHANG Sulin from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, developed an AI platform, KinomeMETA (https://kinomemeta.alphama.com.cn/), for kinase multi-target activity screening. This platform significantly expanded the range of predictable kinase and supported customization by leveraging users' proprietary data.
ZHENG’s group has been dedicated to small molecule kinase inhibitor screening research for years. They previously developed KinomeX, a platform that could predict kinase inhibition profile using multi-task deep neural network, driving advancements in AI technology for kinase activity prediction research. These studies were published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry (2019) and Bioinformatics (2019).
The KinomeMETA platform utilized meta-learning method Reptile and was built upon the molecular feature extraction graph neural network AttentiveFP. By harnessing the rapid adaptation capabilities of meta-learning, KinomeMETA learned patterns of active compounds in different kinases across more than 610,000 active data points.
The platform was constructed through meta-training and fine-tuning processes, comprising two core modules: Customization and Prediction. The Customization module introduced a novel functionality within the field of kinase activity prediction. It allowed users to build new kinase models or enhance predictive capabilities of existing ones using proprietary data, thereby bridging computational and experimental research. The Prediction module could predict inhibition probabilities of compounds against 661 wild-type kinases and clinically relevant kinase mutants. Additionally, the platform provided three result analysis functions: kinase selectivity analysis, molecular property evaluation, and identification of similar kinase inhibitors. These features could assist kinase drug researchers in conducting extended studies.
Researchers further explored the efficiency of KinomeMETA when fine-tuned with experimental data. Building on preliminary findings from KinomeMETA in screening small molecule probes for the "dark" kinase PKMYT1, they utilized the platform's Customization procedure to enhance the default model. Subsequently, the virtual screen by KinomeMETA and experimental validation was conducted for in-house compounds. The results demonstrated that KinomeMETA rapidly improved predictive capabilities with a small number of active compounds, consistently outperforming molecular docking methods.
The KinomeMETA platform offers a Prediction module for kinome activity assessment and a Customization module for efficiently utilizing proprietary data. Through an iterative cycle of dry and wet experiments, it effectively addresses low-data scenarios in drug discovery, significantly accelerating the discovery of novel kinase small molecule probes and druggable kinase targets.
DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae380
Article Link: https://academic.oup.com/nar/advance-article/doi/10.1093/nar/gkae380/7675173
ARTICLE TITLE: KinomeMETA: a web platform for kinome-wide polypharmacology profiling with meta-learning
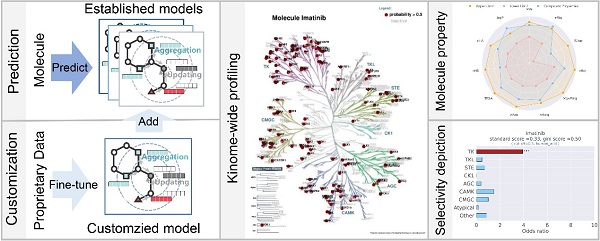
Overview of KinomeMETA platform. (Image by ZHENG Mingyue’s laboratory)
Contact:
JIANG Qingling
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: qljiang@stimes.cn




