Acyl-peptide Hormone Unravels Recognition and Activation Mechanism of Ghrelin Receptor
Ghrelin, also called “the hunger hormone”, is a gastric peptide hormone that regulates food intake, body weight, as well as taste sensation, reward, cognition, learning, and memory. It is featured by its acylation primarily with an octanoic acid at the third amino acid Ser3, which is essential to its binding and physiological functions. The functions of ghrelin are mediated through the ghrelin receptor, a Gq protein-coupled GPCR with high basal activity. The multi-faceted role of ghrelin has made the ghrelin receptor a highly attractive drug target for growth retardation, obesity, and metabolic disorders. However, due to a lack of structural information, the accurate mechanism of recognition and activation of ghrelin receptor by ghrelin remains elusive.
In a study published in Nature Communications on August 20, a joint team of researchers led by JIANG Yi, XIE Xin, and H.Eric XU (XU Huaqiang) from Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica (SIMM) of Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed the mechanism of molecular recognition of ghrelin and activation of the ghrelin receptor.
The researchers solved two cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of Gq-coupled ghrelin receptor bound to ghrelin and a synthetic agonist, GHRP-6, respectively. Combining with functional analyses, the researchers reveal a unique binding pocket for the octanoyl group, which guides the correct positioning of the peptide to initiate the receptor activation.
The researchers also proposed a unique ghrelin receptor activation model. Peptide binding causes steric hindrance to push the side-chain of R283 swinging away from the helix core and to initiate ghrelin receptor activation. They also identified a “hydrophobic lock”, supposed to be responsible for the basal activity of the ghrelin receptor.
These findings enhance our understanding of the molecular basis for acyl-ghrelin recognition and activation of the ghrelin receptor and inspire development of ghrelin receptor-targeting drugs for obesity.
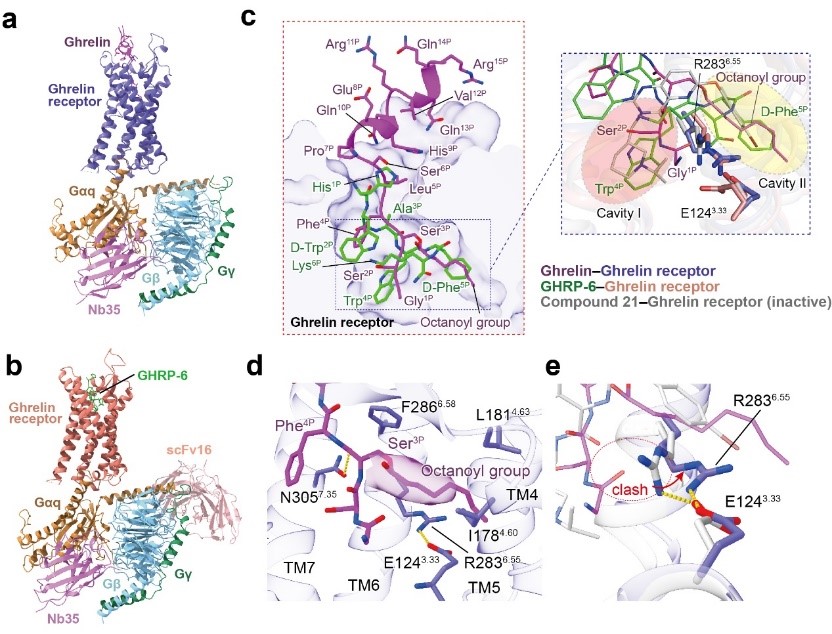
Cryo-EM structures of the Gq-coupled ghrelin receptor bound to ghrelin and GHRP-6 (image by H.Eric XU’s team)
Link:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25364-2
Contact:
DIAO Wentong
Shanghai Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Sciences
E-mail: diaowentong@simm.ac.cn



